Microclimate Report and Reducing the Urban Heat Island
The microclimate report has become a prerequisite for most local and regional planning committees. It has earned the name "Shading and Wind Appendix" because it examines two main aspects: the creation of shade by the planned construction and the phenomenon of increased wind on pedestrians at street level.
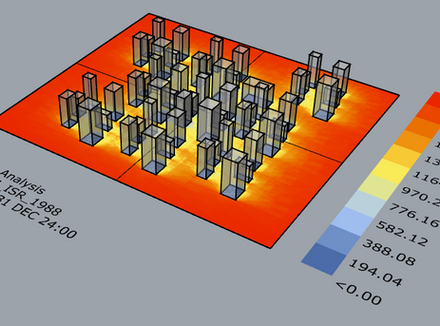
In addition to preparing microclimate reports, we specialize in reducing the effects of the Urban Heat Island in the early planning stages using a unique model we developed.

How Are the Effects of Construction on Shading and Wind Evaluated?
Shading
The way in which buildings cast shadows on their surroundings can have significant consequences, such as affecting passive heating on southern facades of nearby buildings or impairing the efficiency of solar panels and water heaters. Using advanced 3D modeling software, we measure solar radiation around the proposed structure and analyze the building’s impact on these parameters. This technology is also used to design shading in public spaces and create shaded pedestrian pathways.
Wind
A phenomenon known as the "canyon effect" can lead to increased wind speeds in areas between tall buildings. This creates a "wind tunnel" effect, accelerating ground-level winds to speeds that may pose risks to pedestrians. Using a computerized CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) model called "Pedestrian Wind Comfort," we assess wind amplification impacts. If deviations from regulatory standards are identified, we provide recommendations for modifying the building plans.
Reducing the Effects of the Urban Heat Island in the Early Planning Stage
יתרון טכנולוגי בתכנון הסביבתי בעולם שבו דרישות האקלים הולכות ומחמירות, האינטואיציה כבר אינה מספיקה. כדי להבטיח שלקוחותינו יקבלו את התכנון המדויק, הכלכלי והבטוח ביותר, פיתחנו ב"שדות" את A-clim – מנוע אנליטי בלעדי לבחינת היתכנות אקלימית. הטכנולוגיה, אשר פועלת בשימוש פנימי בלבד על ידי מומחי המשרד, מאפשרת לנו לבצע "בקרת איכות" (QA) מדעית לתוכניות בינוי כבר בשלבים הראשוניים ביותר. למה לתכנן איתנו? בעוד שמשרדים אחרים נאלצים להמתין שבועות ליועצים חיצוניים או להסתמך על הערכות גסות, השימוש ב-A-clim מאפשר לצוות שלנו: בדיקת היתכנות מיידית: זיהוי "מוקשים" אקלימיים (כגון חסימות רוח או איי חום קיצוניים) עוד לפני ההגשה לוועדה, וחוסך לכם זמן יקר ותכנון חוזר. אופטימיזציה של זכויות בנייה: היכולת להוכיח מדעית כיצד העמדה נכונה של המבנים מאפשרת ציפוף איכותי מבלי לפגוע בנוחות התרמית. ביטחון סטטוטורי: הגשת נספחים סביבתיים המגובים בנתונים כמותיים וסימולציות מתקדמות, המקלים על הליך הרישוי מול הרשויות. יכולות המערכת (High Level) המערכת משקללת נתונים מטאורולוגיים וגיאומטריים מורכבים לכדי תמונת מצב ברורה, ומסייעת לנו לתת מענה בסוגיות כגון: ניתוח הצללות וחשיפה לקרינה. איתור ופתרון בעיות באוורור המרחב הציבורי. התאמת חומרי הגמר להפחתת עומסי חום. A-clim – השקט הנפשי שלכם, הטכנולוגיה שלנו.